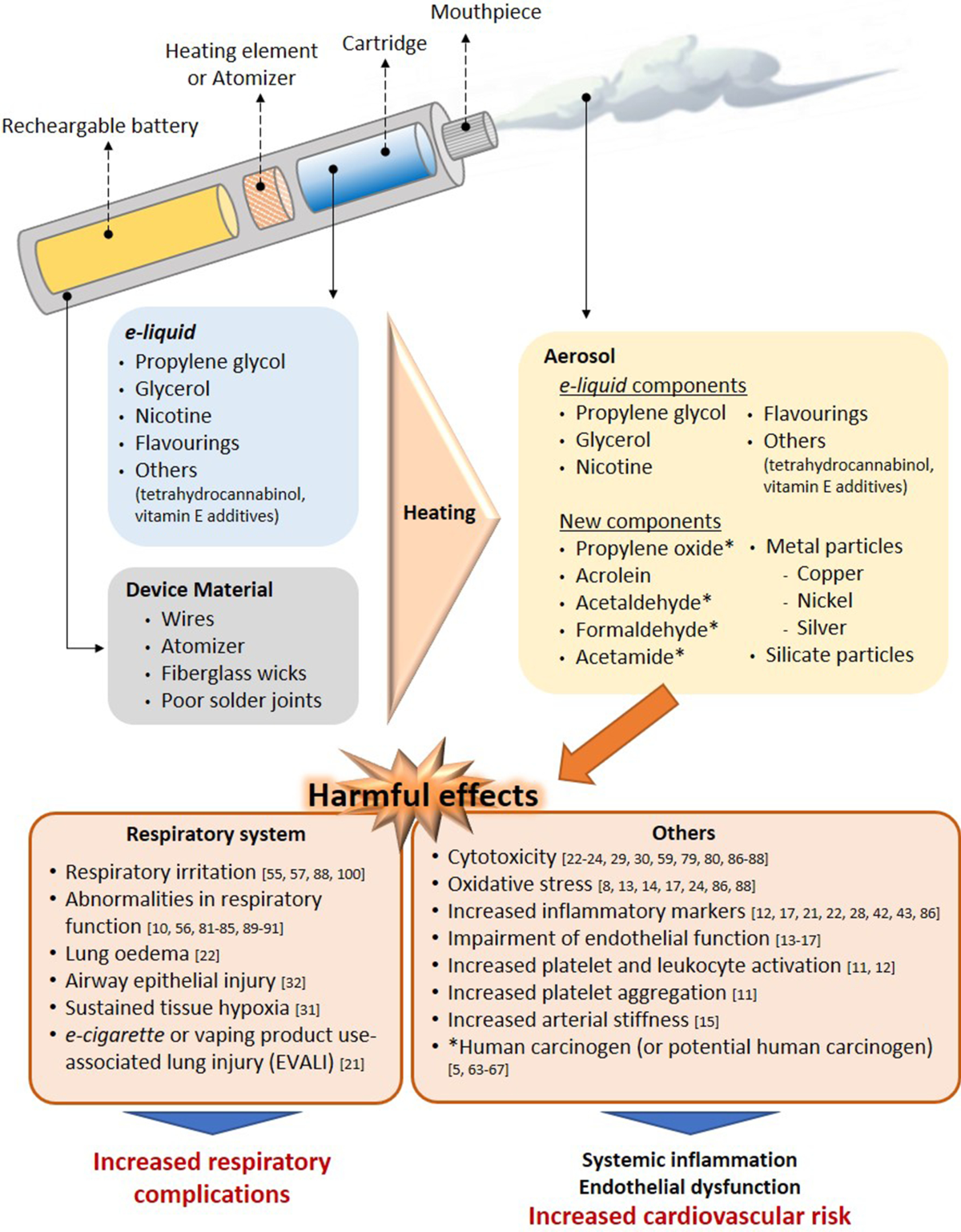
Electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes), also known as vapes, are battery-operated devices that heat a liquid (e-liquid) to produce an aerosol that users inhale.
Components of E-cigarettes
- Battery: Powers the device.
- Heating element (Atomizer): Heats the e-liquid.
- E-liquid Cartridge/Tank: Contains the e-liquid.
- Mouthpiece: Where the user inhales the aerosol.
E-liquids
E-liquids typically contain nicotine, propylene glycol, vegetable glycerin, flavorings, and other additives. Nicotine levels vary widely. Some e-liquids claim to be nicotine-free, but studies have found traces of nicotine in some of these products.
Health Effects
The long-term health effects of e-cigarettes are still being studied. However, evidence suggests potential risks:
- Nicotine Addiction: E-cigarettes can be addictive.
- Respiratory Issues: Vaping can cause lung damage.
- Cardiovascular Effects: E-cigarettes may increase heart rate and blood pressure.
- Exposure to Harmful Chemicals: E-cigarette aerosol can contain harmful chemicals, including heavy metals and carcinogens.
Regulation
E-cigarettes are regulated differently across countries. Regulations often cover aspects such as sales to minors, advertising, and product standards.
Usage Trends
E-cigarette use has increased significantly, especially among young people. This trend raises concerns about nicotine addiction and the potential for young people to transition to traditional cigarettes.
Potential Benefits (with caveats)
Some studies suggest that e-cigarettes may help some smokers quit traditional cigarettes. However, they are not FDA-approved as smoking cessation devices, and more research is needed to determine their effectiveness and safety for this purpose. The best way to quit smoking is to use evidence-based methods recommended by healthcare professionals.
Conclusion
E-cigarettes are not harmless. While they may be less harmful than traditional cigarettes for current smokers who switch completely, they pose significant health risks, especially for young people and non-smokers. Further research and stricter regulations are needed to fully understand and mitigate these risks.










