Traditional cigarettes contain over 7,000 chemicals formed through the combustion of tobacco. Key harmful constituents include:
- Nicotine: The addictive substance found naturally in tobacco.
- Tar: A sticky residue containing numerous carcinogens (cancer-causing agents), like benzene and formaldehyde, deposited in the lungs.
- Carbon Monoxide: A poisonous gas that reduces oxygen delivery in the blood.
- Heavy Metals: Including arsenic, cadmium, and lead.
- Nitrosamines: Potent tobacco-specific carcinogens.
- Oxidant gases and other toxic chemicals.
E-Cigarette (Vape) Ingredients
E-cigarette aerosol is generated by heating a liquid (“e-liquid”). While typically containing fewer substances than cigarette smoke, it is not harmless. Core ingredients include:
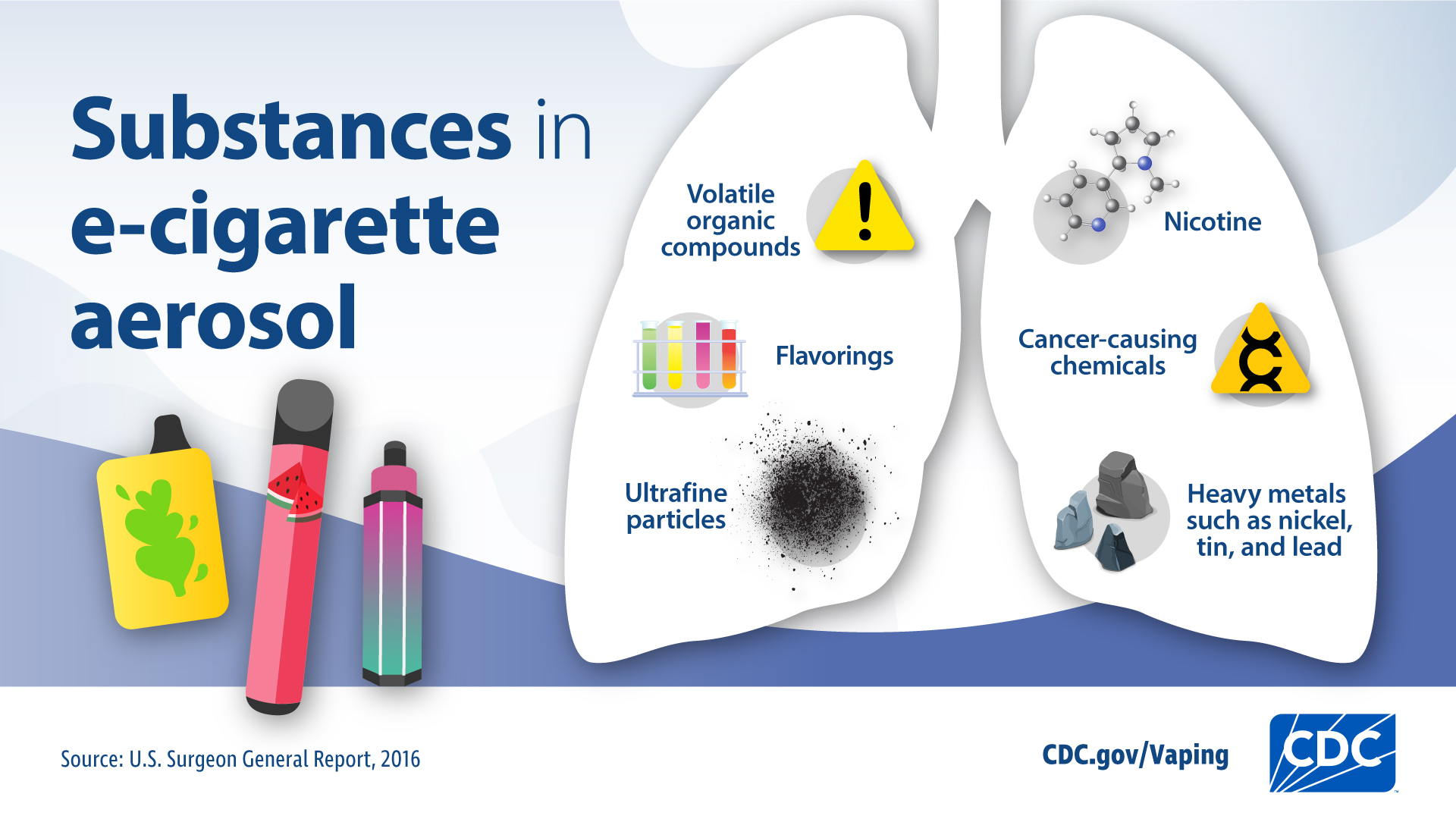
- Propylene Glycol (PG): A common food additive used as a base; vaporizes easily.
- Vegetable Glycerin (VG): Another base liquid, thicker than PG, produces more vapor.
- Nicotine: Extracted from tobacco and added in varying concentrations (including zero-nicotine options).
- Flavorings: Thousands of synthetic or natural compounds. While food-grade, their safety when heated and inhaled is largely unknown.
Additional Considerations
Both products share nicotine addiction risk. Crucially:
E-cigarette vapor contains potentially harmful contaminants: Trace amounts of toxicants like formaldehyde and acetaldehyde can form when e-liquid components are heated (esp. at high temperatures or in degraded devices). Metal particles (e.g., tin, nickel, lead) can leach from the device. Flavorings like diacetyl link to severe lung disease (e.g., “popcorn lung”). Particle pollution is present.
Cigarettes deliver vastly higher levels of carcinogens and toxins due to combustion. However, the long-term health impact of inhaling heated e-liquid ingredients is still under investigation.
Neither product is safe; avoidance is the only risk-free choice.







