Electronic cigarettes (e-cigs) are battery-powered devices that convert e-liquid into inhalable vapor, providing a nicotine alternative without combustion. They rely on three core components: the battery for power, the atomizer for heating, and the cartridge or tank holding the e-liquid.
How Electronic Cigarettes Work
When activated (often by inhaling or pressing a button), the battery sends an electrical current to the atomizer’s coil. This coil heats the e-liquid-soaked wick, vaporizing it into a fine aerosol. Users inhale this vapor, which delivers nicotine and flavorings. The process avoids burning tobacco, reducing tar and carbon monoxide compared to traditional cigarettes.
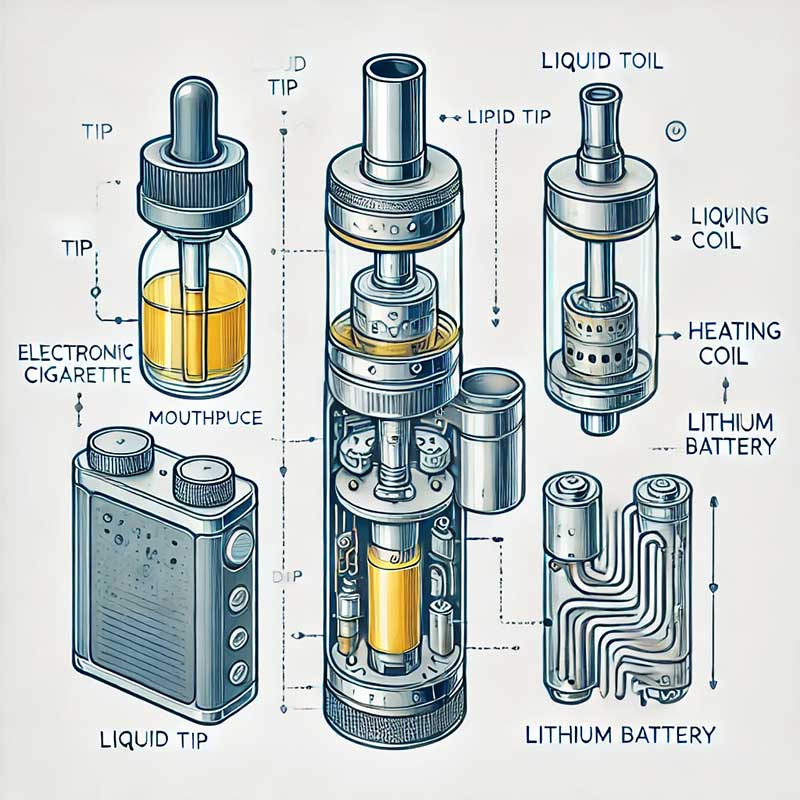
Key elements include adjustable settings like voltage or wattage to control vapor production and temperature. Advanced models feature airflow controls and safety mechanisms such as short-circuit protection.
ECig Starter Tips
- Choose the right device: Beginners should opt for simple pod systems or starter kits with user-friendly features over complex mod setups.
- Select appropriate e-liquid: Start with lower nicotine strengths (e.g., 3-6mg/mL) and standard ratios like 50/50 PG/VG for balanced throat hit and vapor.
- Prime the coil: Always saturate new coils with e-liquid before use to prevent dry burns and extend atomizer life.
- Maintain battery safety: Use the correct charger, avoid overcharging, and store batteries away from heat to prevent malfunctions.
- Practice proper hygiene: Clean tanks regularly with warm water to avoid residue buildup and ensure consistent flavor.
- Seek guidance: Consult reliable resources or experienced users for personalized advice on device care and troubleshooting.










