How an Electronic Cigarette Works
An electronic cigarette (e-cigarette) operates through a vaporization process, where a battery heats an e-liquid within an atomizer to produce an aerosol for inhalation. This aerosol mimics the sensation of smoking without combustion or tobacco burn.
Key stages involve battery activation, liquid heating (typically to 200-300°C), and vapor formation. As a user inhales, airflow sensors trigger the device, ensuring efficient delivery without open flames.
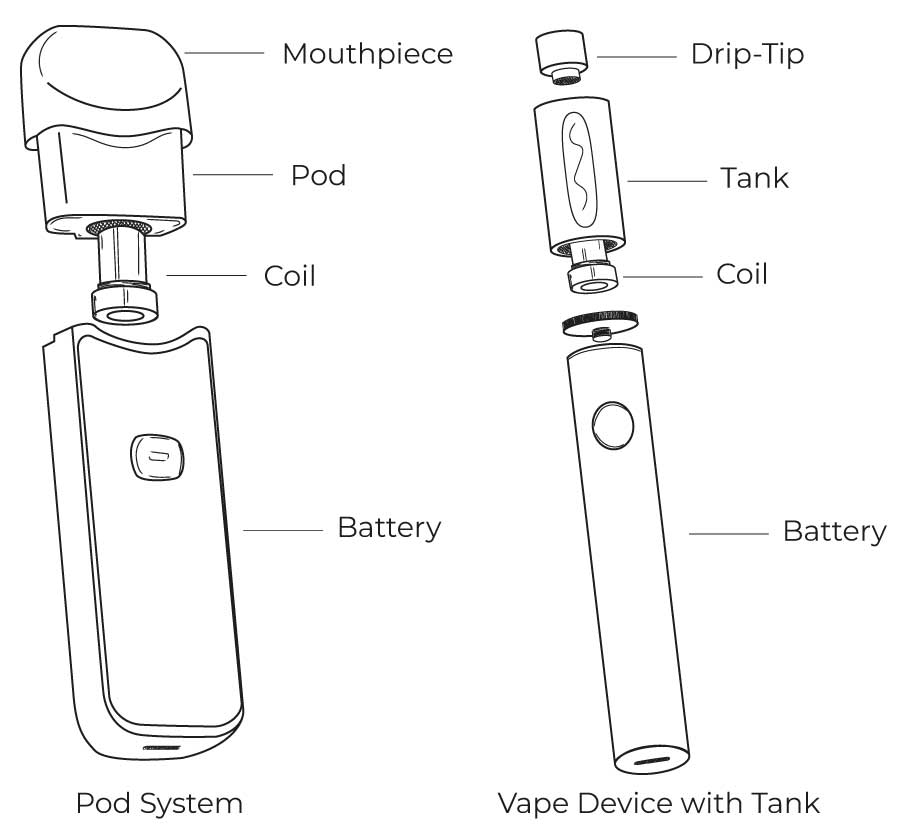
Essential Components Explained
E-cigarettes consist of three main parts, each vital for functionality:
- Battery: Provides power to the device; rechargeable via USB or similar ports.
- Atomizer: Contains a coil that heats e-liquid upon activation.
- E-Liquid Tank/Cartridge: Holds nicotine-infused liquid (often with flavors), which is drawn into the atomizer.
Beginner-Friendly User Guide
Follow these steps for safe and effective e-cigarette use as a beginner:
- Assemble Components: Securely connect the battery to the atomizer and fill the tank with e-liquid.
- Power On: Activate the device via a button or inhale, depending on model.
- Inhale Properly: Draw slowly for 3-5 seconds, allowing vapor to build.
- Maintain Regularly: Clean atomizer coils weekly and charge the battery as needed.
Avoid overfilling and store e-liquid away from heat; replace parts when performance declines to ensure optimal experience.










