Electronic cigarette use has been associated with fatalities, primarily linked to acute severe lung injury and other specific conditions.
Confirmed Deaths: EVALI Outbreak
The largest cluster of documented e-cigarette-related fatalities occurred during the 2019-2020 EVALI (E-cigarette or Vaping product use-Associated Lung Injury) outbreak in the United States.
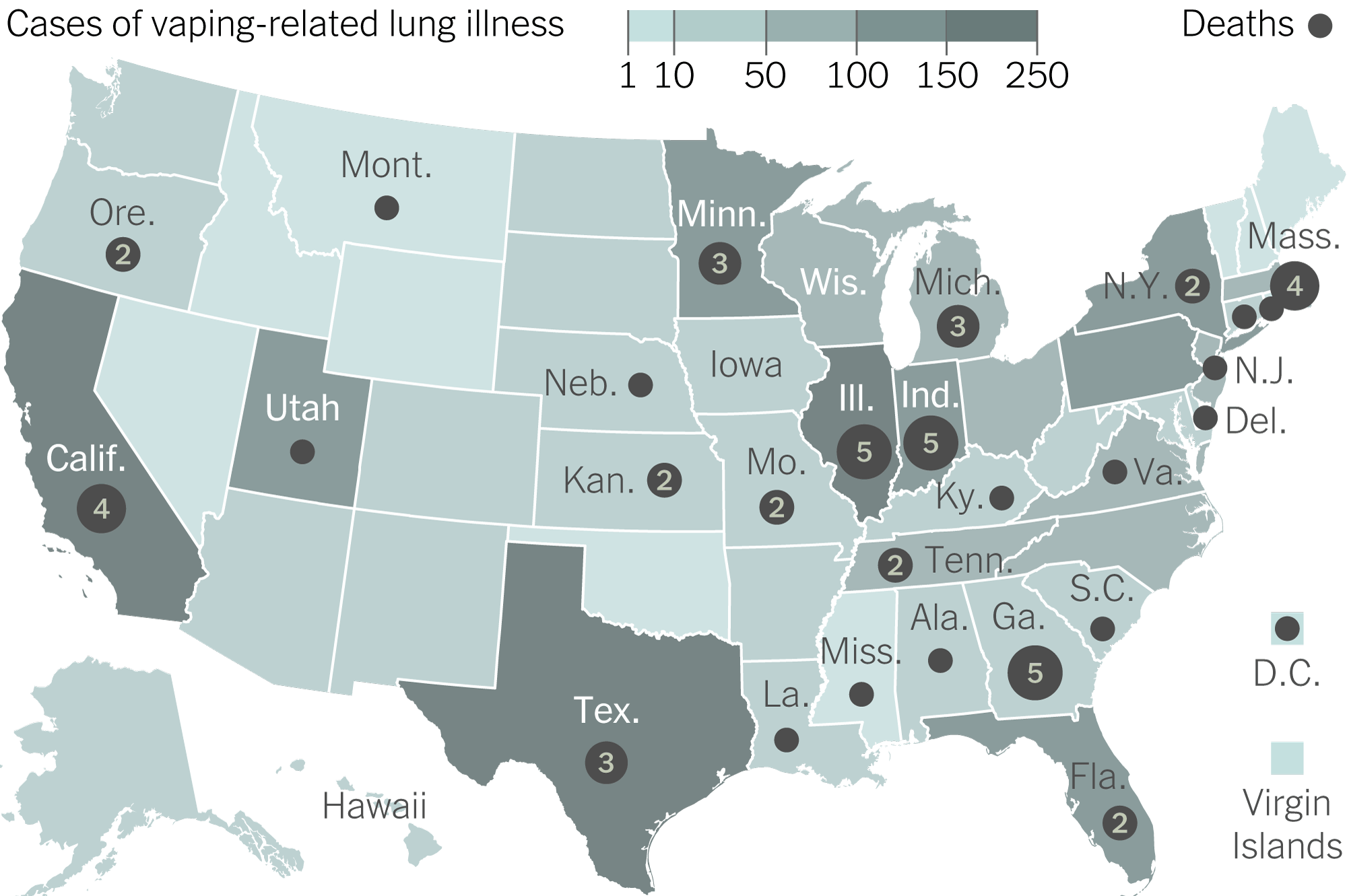
- CDC Confirmed Deaths: 68 deaths were formally confirmed across 29 states and the District of Columbia.
- Primary Culprit: Vitamin E acetate (VEA), used as a thickening agent in illicit THC-containing vaping products, was strongly identified as the cause of these specific lung injuries and deaths.
- Mechanism: VEA, when inhaled, disrupts normal lung function, leading to severe chemical pneumonitis and respiratory failure.
Other Potential Causes of Death
While EVALI was a specific outbreak, other potential mechanisms for e-cigarette-associated mortality exist:
- Explosions/Burns: Malfunctioning lithium-ion batteries causing device explosions have resulted in traumatic injuries and rare fatalities.
- Toxic Exposure: Acute nicotine poisoning, particularly involving ingestion of e-liquids by children, can be lethal. Accidental intravenous injection of concentrated nicotine has also caused death.
- Cardiovascular Events: Nicotine significantly increases heart rate and blood pressure. While long-term cardiovascular mortality risk is still under investigation, it theoretically elevates risk for individuals with severe underlying heart disease. Acute cardiovascular events temporally associated with vaping have been reported but definitive causation is complex.
- Underlying Respiratory Disease: Vaping can exacerbate conditions like asthma, potentially leading to severe attacks.
Important Distinctions
Long-Term Cancer/COPD Risk vs. Combustible Tobacco:
- E-cigarettes expose users to fewer carcinogens and toxicants than combustible cigarettes.
- The long-term cancer and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) mortality risk profile is expected to be significantly lower than that of smoking traditional cigarettes, though decades-long data are not yet available.
- Switching completely from smoking to e-cigarettes reduces exposure to major tobacco-related toxins.
Youth and Non-Smokers:
- E-cigarette use poses significant health risks, particularly to adolescents whose brains are still developing.
- Nicotine addiction is the primary concern for youth and non-smokers, potentially acting as a gateway to tobacco use.
Key Takeaways on Fatalities
- EVALI deaths (68) were directly caused by inhaling Vitamin E acetate, primarily from illicit THC vapes.
- Other rare, isolated deaths have occurred due to device explosions, acute nicotine poisoning (usually ingestion), or possibly severe exacerbations of underlying conditions.
- E-cigarettes are not risk-free.
- Long-term mortality risks compared to combustible tobacco are predicted to be substantially lower but are not yet fully quantified.
- They are unsafe for youth, young adults, pregnant women, and non-smokers.









