Studies on Electronic Cigarettes
Numerous studies investigate the health impacts and efficacy of electronic cigarettes. Key findings suggest potential benefits for smoking cessation but highlight significant risks. For instance, research published in the New England Journal of Medicine indicates that e-cigarettes may aid in quitting smoking compared to traditional nicotine replacement therapy. However, other studies, such as those from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, emphasize concerns about nicotine addiction, lung injuries like EVALI, and unknown long-term effects. Meta-analyses reveal that while e-cigarettes could reduce exposure to some tobacco toxins, cardiovascular and respiratory risks persist, requiring ongoing scrutiny.
Cost Comparison: Vaping vs. Smoking
Financial analysis consistently shows that vaping generally costs less than smoking over the long term, though initial investments vary. Typical calculations for a moderate user include:
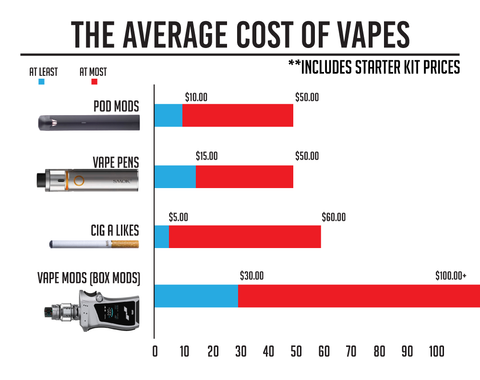
- Initial setup: An e-cigarette starter kit ranges from $20 to $100, versus no upfront cost for cigarettes.
- Recurring expenses: A month’s supply of e-liquids or pods averages $30-$60, while a pack-a-day smoker spends $200-$300 monthly on cigarettes.
Overall savings can reach 50-70% annually with vaping, based on data from consumer reports and health economics reviews. However, individual costs fluctuate due to usage patterns and regional taxes.