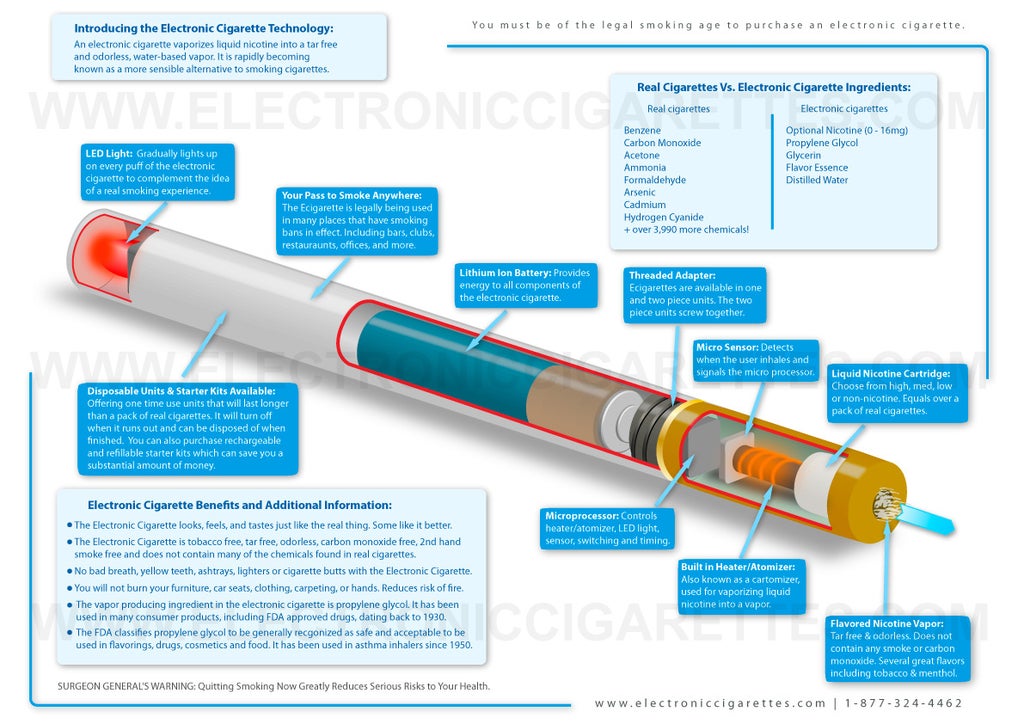
The terms “cigarettes,” “vapor,” and “electronic” are often used when discussing smoking and alternatives. Here’s a breakdown:
Cigarettes
- Traditional Cigarettes: These are tobacco-filled cylinders that are burned and inhaled. They contain nicotine, a highly addictive substance, and numerous harmful chemicals produced by combustion.
- Health Risks: Cigarette smoking is a leading cause of lung cancer, heart disease, stroke, and other serious health problems.
Vapor (Vaping)
- Refers to: The aerosol produced by electronic cigarettes or vaping devices. This aerosol often contains nicotine, flavorings, and other chemicals.
- How it Works: Vaping devices heat a liquid (e-liquid) to create a vapor that is inhaled.
Electronic Cigarettes (E-cigarettes)
- Definition: Battery-operated devices that heat a liquid to produce an aerosol for inhalation. They are designed to mimic the experience of smoking traditional cigarettes.
- Components: Typically consist of a battery, heating element (atomizer), and a cartridge or tank that holds the e-liquid.
- E-liquid Contents: E-liquids generally contain nicotine, propylene glycol, vegetable glycerin, flavorings, and other additives. The nicotine content varies.
- Health Considerations: While often marketed as a safer alternative to cigarettes, e-cigarettes still pose health risks. The long-term effects of vaping are still being studied. Concerns include potential lung damage, nicotine addiction, and exposure to harmful chemicals.
Key Differences: Cigarettes involve burning tobacco, whereas e-cigarettes heat a liquid. E-cigarettes generally expose users to fewer harmful chemicals than cigarettes, but they are not risk-free.