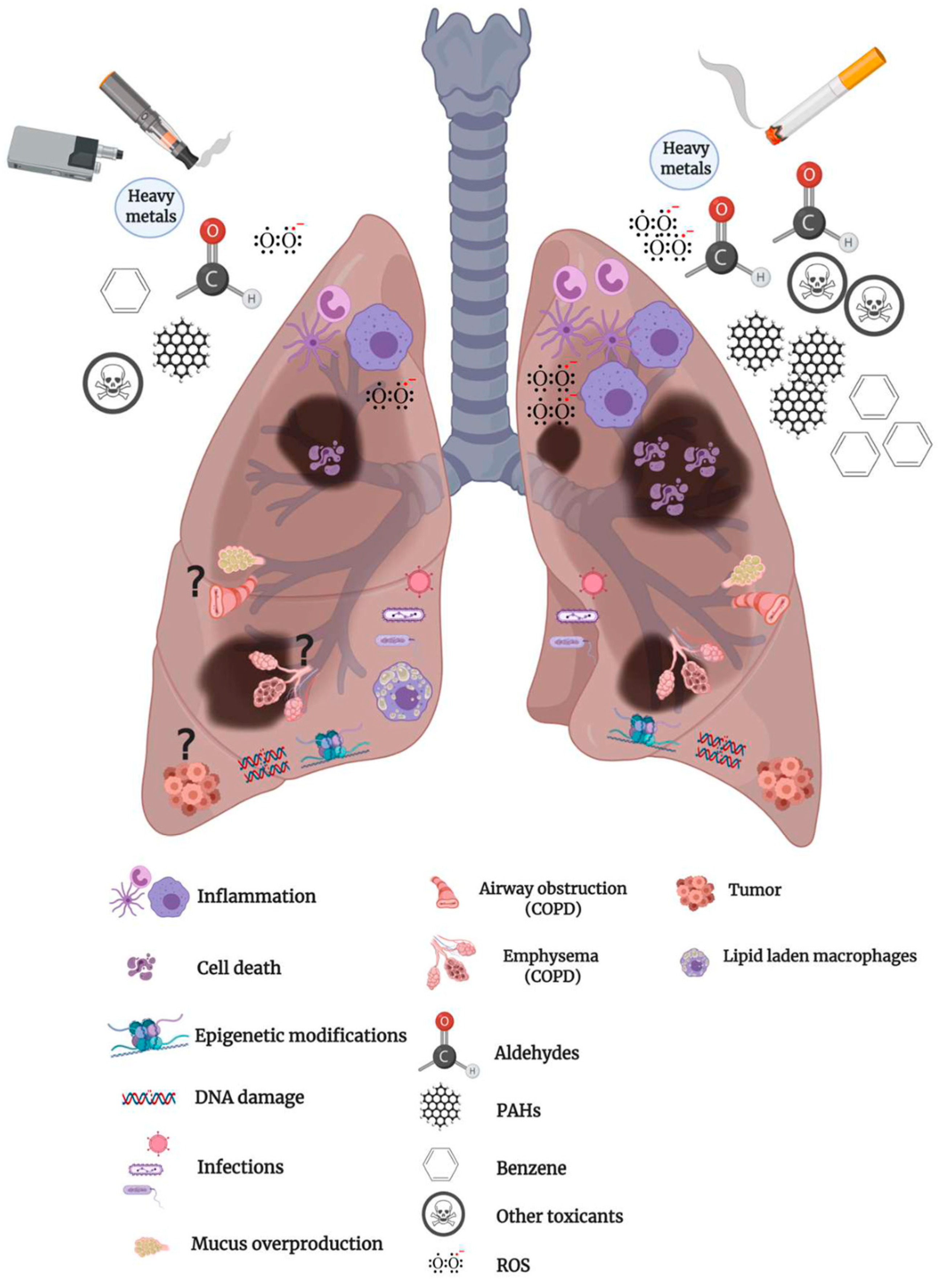
The health effects of electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) are a subject of ongoing research and debate. While often marketed as a safer alternative to traditional cigarettes, they are not without potential risks.
Respiratory System
- Lung Damage: E-cigarette use can cause lung inflammation and damage. Studies have linked vaping to an increased risk of chronic lung diseases like bronchiolitis obliterans.
- Asthma and Bronchitis: Vaping can exacerbate existing respiratory conditions such as asthma and bronchitis.
- Popcorn Lung: Some e-liquids contain diacetyl, a chemical linked to bronchiolitis obliterans, also known as “popcorn lung.”
Cardiovascular System
- Increased Heart Rate and Blood Pressure: Nicotine in e-cigarettes can elevate heart rate and blood pressure, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Arterial Stiffness: Vaping may contribute to arterial stiffness, a precursor to heart attacks and strokes.
Neurological Effects
- Nicotine Addiction: E-cigarettes contain nicotine, which is highly addictive. This can lead to dependence and withdrawal symptoms.
- Brain Development: Nicotine can harm brain development in adolescents and young adults, affecting memory, attention, and learning.
Other Potential Health Effects
- Exposure to Harmful Chemicals: E-cigarette aerosol can contain harmful chemicals, including heavy metals, volatile organic compounds, and ultrafine particles.
- Secondhand Exposure: Secondhand e-cigarette aerosol can expose bystanders to nicotine and other harmful substances.
- Unknown Long-Term Effects: The long-term health effects of e-cigarette use are still largely unknown, as they haven’t been studied extensively over many years.
It is important to note that e-cigarettes are not harmless, and more research is needed to fully understand their long-term health consequences.